Obesity has become a significant public health concern in the United States, but it can range in severity. When we discuss morbid obesity, we’re talking about a condition that carries more serious health implications and a bigger impact on quality of life.
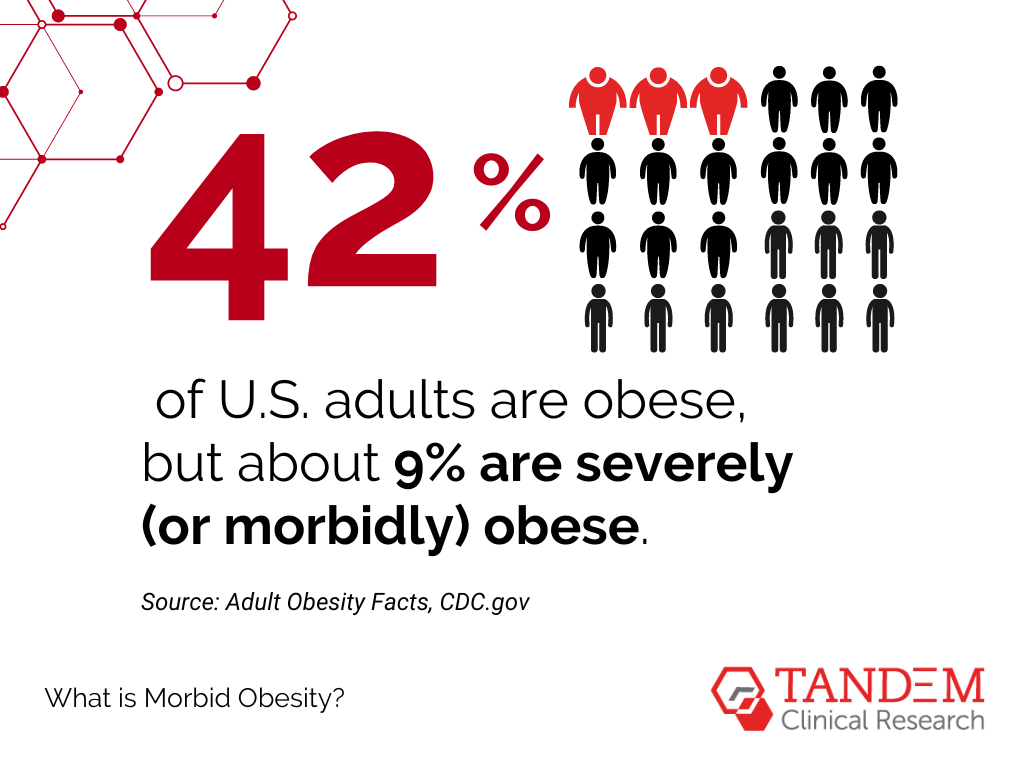
In fact, the CDC estimates that about 42% of U.S. adults are obese, but about 9% are severely (or morbidly) obese.
At Tandem Clinical Research, we are dedicated to advancing medical understanding and treatments for complex conditions like morbid obesity. We believe in providing exemplary patient support while working toward a brighter future together.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into morbid obesity, why it matters, and how ongoing research can offer hope and opportunities to lose weight safely.
Understanding Morbid Obesity
What is morbid obesity? Typically, it’s defined as having a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 or higher or a BMI of 35 or higher with obesity-related health conditions. Both of these measurements represent a severe and potentially life-threatening level of excess body fat.
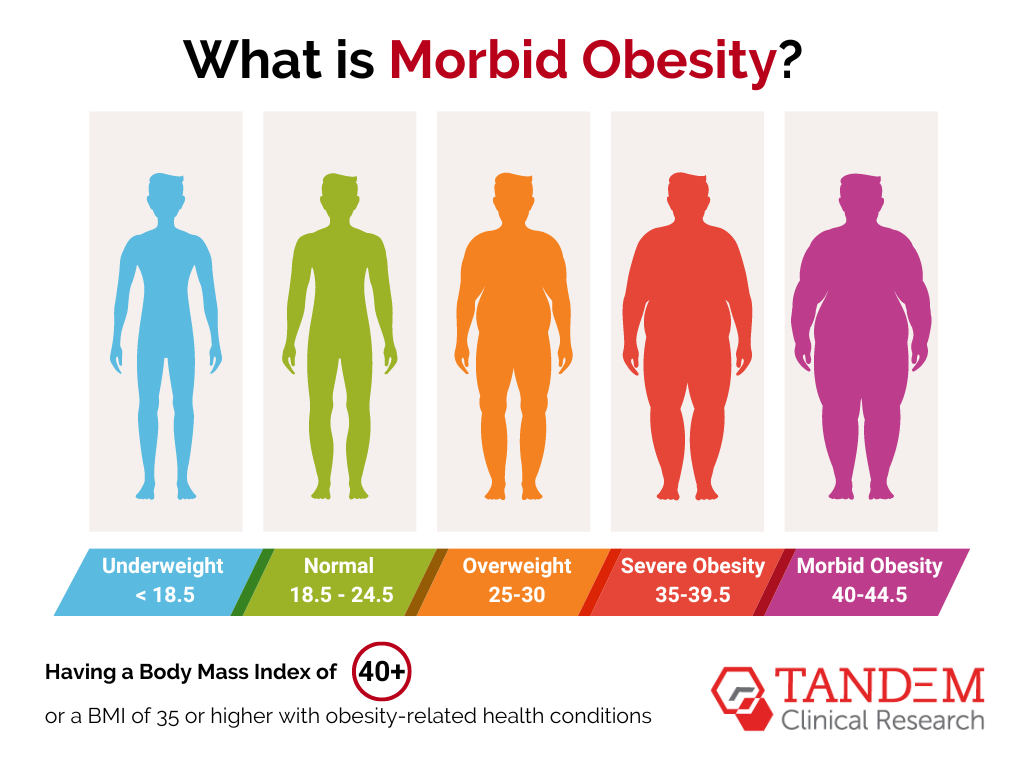
This condition is characterized not only by a high degree of body fat but also by its significant impact on overall health. Individuals with severe obesity face an increased risk of developing severe health problems, as well as debilitating complications and significantly reduced life expectancy.
In short, morbid obesity is a critical public health concern. Its severity often necessitates intensive medical intervention and management strategies, such as advanced medications, surgical options, and comprehensive lifestyle changes.
The extreme nature of severe obesity exacerbates the strain on bodily systems, making it a more urgent and complex issue to address, both from a medical and a quality-of-life perspective.
Health Risks Associated with Morbid Obesity
As mentioned previously, severe obesity poses a significant risk for a range of serious health conditions, making it a significant concern. Most commonly, severe obesity is associated with:

Cardiovascular Diseases
It’s well known that individuals with morbid obesity are at a higher risk for cardiovascular diseases. Excess body weight strains the heart and can lead to conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, and high blood pressure, which can cause strokes.
Considering that heart disease is the leading cause of death in both U.S. men and women, this is an especially concerning risk for people with excessive body fat.
Type 2 Diabetes
Severe obesity is a major risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. According to the UCSF Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery Program, about 80% of people with type 2 diabetes are overweight, and the higher your Body Mass Index, the more significant your risk becomes.

Excess fat can lead to insulin resistance, where the body does not use insulin effectively, resulting in high blood sugar levels. This can cause:
- Neuropathy: Nerve damage that can lead to pain, numbness, or tingling.
- Retinopathy: Damage to the blood vessels in the eyes, which can lead to vision problems.
- Kidney Damage: Compromised kidney function and potential kidney failure.
Respiratory Issues
Generally, severe obesity is associated with reduced airflow, increased airway hyperresponsiveness, and an increased risk of conditions such as pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary embolism.
In simpler terms, excessive body fat can make it harder to breathe while active and resting.
As Hopkins Medicine states, obesity is common in sleep apnea patients, whose airways become blocked during sleep and lead to interrupted breathing. Severe obesity is also highly related to an increased risk of asthma, which can make living an active lifestyle even more challenging.
Certain Cancers
Severe obesity is associated with an increased risk of several types of cancer. The CDC states that having obesity is linked with a higher risk of getting 13 types of cancers, including:
- Adenocarcinoma of the esophagus
- Breast (particularly in women post-menopause)
- Colon and rectum
- Uterus.
- Gallbladder
- Upper stomach
- Kidneys
- Liver
- Ovaries
- Pancreas
- Thyroid
- Meningioma
- Multiple myeloma
A BMI of 40.0 or higher does not guarantee that you will develop any of these cancers (or others), but it does increase your overall risk of cancer.
The Impact of Morbid Obesity on Quality of Life

Severe obesity affects more than just physical health – it can also have a substantial impact on an individual’s emotional well-being, social life, and overall quality of life.
Many people with severe obesity experience:
Reduced Mobility and Physical Limitations
Excess weight can limit mobility and make physical activities more challenging. This can lead to increased stress on joints, difficulty in daily activities, and challenges in performing tasks such as walking or climbing stairs.
According to a 2023 study from Obesity Science & Practice, adults with obesity spend more time being sedentary than adults with a healthy body weight – about 6 hours per day rather than an average of 1.88 hours.
Social Stigma and Discrimination
Social stigma and discrimination associated with obesity can affect employment opportunities, personal relationships, and even the quality of healthcare that individuals receive.
Unfortunately, discrimination against Americans with obesity has continued to grow over the last few decades. As the National Council on Aging (NCOA) states, as obesity rates rise, weight discrimination also increases.
Mental Health Challenges
Last but certainly not least, the psychological impact of morbid obesity can be pervasive and long-lasting. Mental illness and obesity often co-occur, which can necessitate a multi-pronged approach to treatment.
According to the Stop Obesity Alliance, people with depression are more likely to experience obesity, and vice versa. High rates of obesity have also been studied in populations with mood disorders, schizophrenia, ADHD, anxiety disorders, disordered eating, and trauma.
More generally, many people battling obesity struggle with feelings of low self-esteem and social isolation. Others experience persistent concerns about their appearance, health, and weight, which can impact their sense of self-worth and emotional wellness.
How Clinical Research Trials Are Making a Difference

At Tandem Clinical Research, we recognize the multifaceted nature of morbid obesity and the need for comprehensive solutions. This isn’t just a physical condition; it’s a mentally draining, emotional, and life-changing situation.
Our mission is to connect individuals with groundbreaking clinical trials that focus on innovative treatments and interventions for severe obesity. Through our efforts, ongoing research is continually…
1. Exploring New Medications
Medications are a vital component of managing severe obesity. Research in this area focuses on developing new drugs, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and other novel compounds, to help with weight management.
Today, many researchers are also investigating the effectiveness of combining different medications to enhance weight loss and improve patient outcomes.
2. Advancing Surgical Options
Bariatric surgery can be life-changing for individuals with morbid obesity. Many research trials are focused on improving minimally invasive procedures such as laparoscopic gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy. They also study the long-term effects of surgical interventions on weight loss, metabolic health, and overall quality of life.
3. Exploring Behavioral and Lifestyle Interventions
Managing morbid obesity often requires lifestyle changes. As a result, it’s common for clinical trials to evaluate new approaches to support behavior change, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and motivational interviewing.
People with severe obesity may also benefit from participating in trials for nutrition and exercise programs. This clinical research tests the effectiveness of various diet and physical activity regimens to determine the best strategies for losing weight and maintaining a healthy body fat percentage.
4. Researching Genetic and Biological Factors
The better we understand the genetic and biological factors influencing obesity, the sooner we can develop and enact personalized treatment approaches. Researchers are currently studying the genes associated with obesity to develop targeted therapies and explore how individual metabolism affects weight management.
Learn If You Qualify for a Morbid Obesity Clinical Study
If you or someone you know is struggling with severe obesity, participating in clinical research could be a vital step toward finding effective solutions and preventing other long-term health problems.
At Tandem Clinical Research, we are committed to connecting individuals with trials that could improve their lives and the lives of others.
When you participate in a clinical trial, you don’t just contribute to scientific progress. You also receive valuable access to cutting-edge treatments and expert care that can make an immense difference in your life.
To explore current clinical trials related to obesity or to learn more about how you can get involved, get in touch. We work with all types of individuals in Florida, Louisiana, and New York.
Sources:
UCSF Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery Program
The Dangers of Uncontrolled Sleep Apnea, Hopkins Medicine
How Do Weight Bias and Stigma Affect Patients With Obesity? – National Council on Aging (NCOA)
Fast Facts – Mental Health and Obesity – Stop Obesity Alliance