Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) is a complex and debilitating neurodegenerative disorder that affects millions of individuals and their families worldwide. Often underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed, LBD poses significant challenges for both patients and caregivers. Although LBD can affect both men and women, certain studies indicate a marginally higher occurrence in men.
Clinical research is at the forefront of unraveling the mysteries of LBD, providing hope for improved diagnosis, treatment, and, ultimately, a better quality of life for those living with this condition. In this blog, we will delve into the world of Lewy Body Dementia, explore its characteristics, and highlight the pivotal role of clinical research in advancing our understanding and management of this disease.
Understanding Lewy Body Dementia
Lewy Body Dementia is a progressive brain disorder characterized by the accumulation of abnormal protein deposits called Lewy bodies in the brain’s nerve cells. These deposits disrupt communication between brain cells, leading to a wide range of cognitive, motor, and psychiatric symptoms. LBD is often divided into two main subtypes:
1. Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB): This subtype primarily manifests with cognitive symptoms similar to Alzheimer’s disease but also includes visual hallucinations, fluctuating alertness, and motor symptoms like parkinsonism.
2. Parkinson’s Disease Dementia (PDD): Initially, individuals with Parkinson’s disease develop movement symptoms and, later, cognitive symptoms, which can evolve into dementia.
The Impact of LBD

The impact of LBD extends far beyond the individuals diagnosed with the condition, profoundly affecting their families as well. The emotional toll on loved ones is significant, as they witness the steady cognitive and physical decline of their family member. Caregivers often report feelings of stress, anxiety, and depression, given the 24/7 care that LBD patients may require.
From a financial perspective, the costs associated with managing LBD are considerable. These include direct expenses, such as medical and long-term care, and indirect costs, like lost income — both from the patient and the caregiver who may need to reduce work hours or leave employment entirely.
The burden of LBD underscores the urgent need for more effective treatments. Clinical research is the key to developing these much-needed therapies. Through clinical trials, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the disease, which can lead to the development of innovative treatments and, potentially, a cure. It’s through this continued exploration and discovery that we can provide hope for those affected by LBD and their families.
Causes and Risk Factors
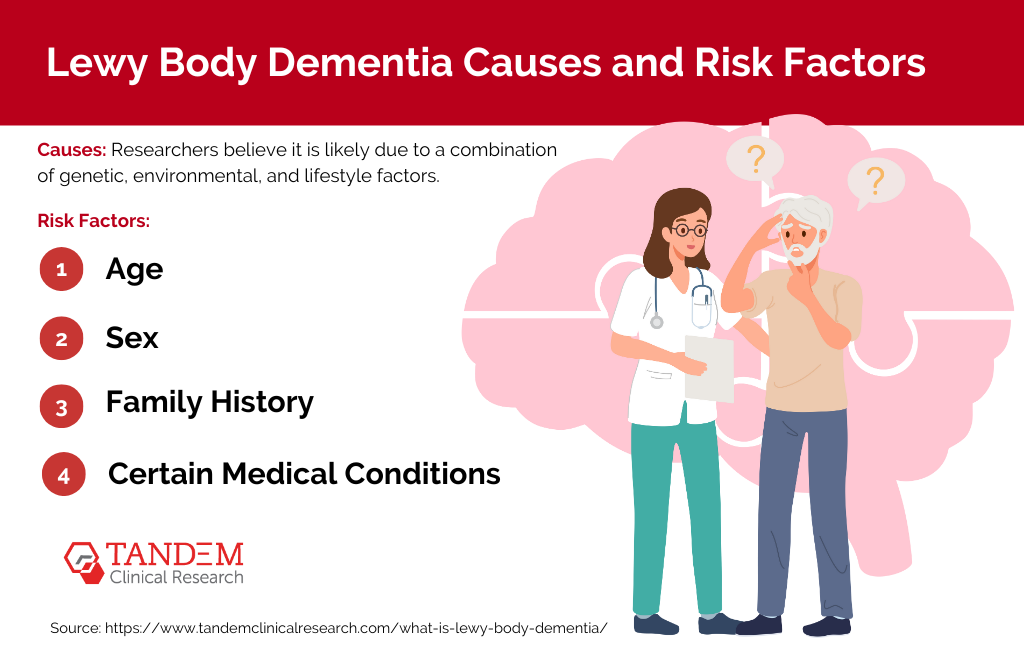
The exact causes of Lewy Body Dementia remain unknown; however, researchers believe it is likely due to a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Like many other neurodegenerative disorders, the presence of Lewy bodies, which are protein deposits, in the brain is a hallmark feature of LBD. These Lewy bodies accumulate in areas of the brain responsible for behavior, cognition, and movement, causing the symptoms associated with the disease. While the reason for this build-up is still under investigation, certain risk factors have been identified:
- Age: The risk of developing LBD increases with age, with most people diagnosed being over the age of 50.
- Sex: Males are slightly more likely to develop LBD than females.
- Family History: Individuals who have a family member with LBD or Parkinson’s disease are at a higher risk of developing the disease.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions like Parkinson’s disease or REM sleep behavior disorder can increase the risk of LBD.
It’s important to note that these risk factors do not guarantee the development of LBD, but merely increase the likelihood. Ongoing research is crucial in identifying the exact causes and developing effective treatments for LBD.
Lewy Body Dementia Signs and Symptoms
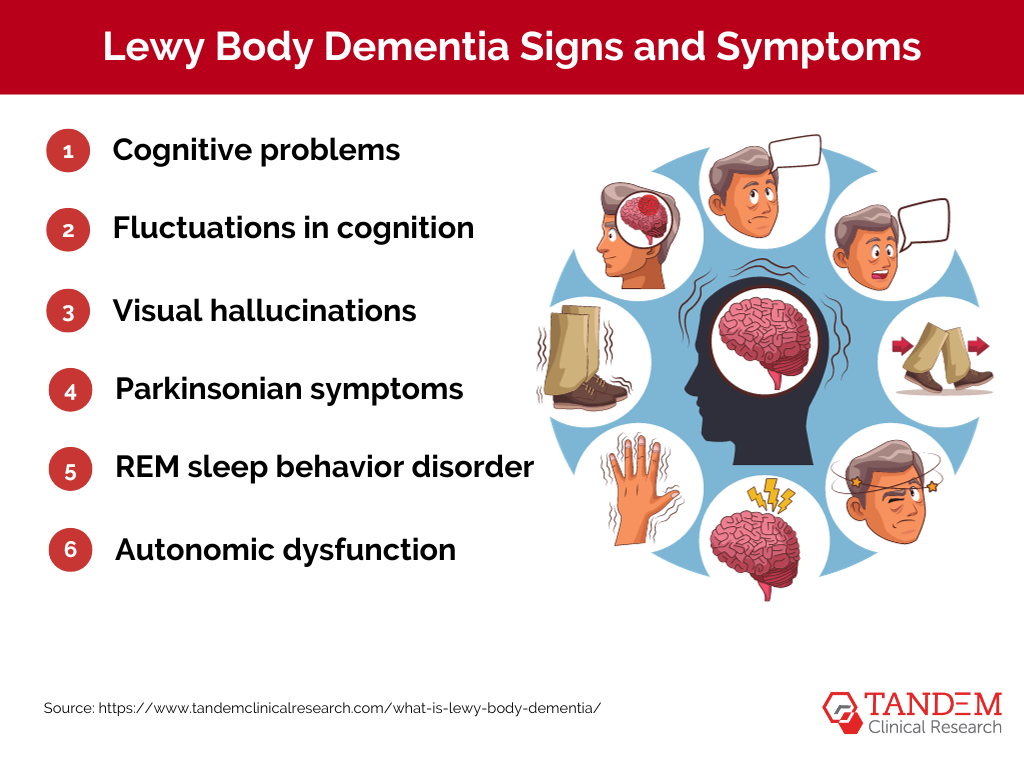
Lewy Body Dementia’s signs and symptoms can be quite diverse, often resembling those of other neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. This overlap can make diagnosis challenging. However, certain characteristic signs and symptoms can help differentiate LBD:
1. Cognitive problems: Similar to Alzheimer’s disease, people with LBD often experience significant cognitive issues. These can include memory loss, difficulty with visual-spatial tasks (like puzzles), and problems with planning, problem-solving, and focusing attention.
2. Fluctuations in cognition: Unlike most other forms of dementia, individuals with LBD often have good days and bad days in terms of their cognitive function. On good days, they may appear almost normal, while on bad days, they may struggle with basic tasks and behaviors.
3. Visual hallucinations: These are common symptoms of LBD, with individuals often seeing things that aren’t there, like animals, people, or objects. These hallucinations can be very vivid and detailed.
4. Parkinsonian symptoms: Symptoms similar to those of Parkinson’s disease are common in LBD, including slow movement, shuffling walking, and muscle stiffness. Some people may also have blank facial expressions and difficulties with balance.
5. REM sleep behavior disorder: People with LBD often act out their dreams during REM sleep, sometimes violently. This disorder may occur years before any cognitive symptoms of LBD appear.
6. Autonomic dysfunction: This involves disruptions in automatic bodily functions like blood pressure control, temperature regulation, and bladder and bowel function.
It is important to note that not every individual with LBD will experience all these symptoms, and the severity can vary significantly between individuals. Anyone experiencing these symptoms should consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and potential referral to a neurologist or other specialist.
Managing Lewy Body Dementia

Management of Lewy Body Dementia primarily revolves around providing supportive care and symptom relief, as there is currently no cure for the disease. Treatment strategies are often multidimensional, encompassing medical, physical, and emotional aspects:
1. Medication: Several medications may be used to manage the symptoms of LBD. These often include drugs used to treat Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, as well as medications for addressing mood changes, hallucinations, and other psychiatric symptoms. It’s important to note that response to medications can vary greatly among individuals and that some drugs can potentially worsen certain symptoms.
2. Physical Therapy: Regular physical activity can help manage motor symptoms, improve mood, and enhance overall wellbeing. Physical therapy may include exercises for flexibility, strength, gait, and balance.
3. Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapists can assist individuals in adapting to their living environment and maintaining their daily living skills as long as possible. This may include strategies for personal care, home safety, memory aids, and assistive devices.
4. Speech and Language Therapy: For individuals experiencing communication difficulties or swallowing problems, speech and language therapy can be beneficial.
5. Supportive Services: Psychological counseling, support groups, respite care, and other services can be invaluable in helping patients and their families cope with the emotional challenges associated with LBD.
It’s crucial to remember that each individual’s journey with LBD is unique, and what works well for one person may not work as well for another. Therefore, it is essential to have open, ongoing communication with healthcare providers to tailor a management plan that best meets the needs of the individual and their family.
The Importance of Clinical Research
Clinical research serves as the backbone of our understanding of LBD. It encompasses a wide range of studies aimed at:
1. Early Diagnosis: Early detection of LBD is challenging but crucial. Clinical research seeks to identify biomarkers and develop reliable diagnostic tools to differentiate LBD from other neurodegenerative conditions.
2. Treatment Development: Currently, there is no cure for LBD, and treatment is primarily focused on symptom management. Clinical trials explore potential medications and therapies targeting the underlying mechanisms of the disease.
3. Improving Care: Research is ongoing to develop comprehensive care guidelines and strategies tailored to the unique needs of LBD patients and their caregivers.
Promising Areas of LBD Research
1. Neuroimaging: Advanced brain imaging techniques, such as PET and MRI scans, are helping researchers visualize and track the progression of Lewy bodies in the brain, aiding in early diagnosis.
2. Genetic Studies: Investigating the genetic factors contributing to LBD helps identify risk factors and potential therapeutic targets.
3. Biomarkers: Researchers are working to identify reliable biomarkers in blood or cerebrospinal fluid that can aid in diagnosing LBD and monitoring disease progression.
4. Clinical Trials: Numerous clinical trials are underway to test new medications and interventions aimed at alleviating LBD symptoms and slowing their progression.
5. Caregiver Support: Research is focusing on developing resources and support systems for caregivers who play a crucial role in the well-being of LBD patients.
The Role of Participants in Clinical Trials
The success of clinical research relies on the participation of individuals with LBD and their caregivers. By volunteering for clinical trials, patients and their families contribute to the development of better treatments and a deeper understanding of the disease. Participation in trials can also provide access to potential cutting-edge therapies that may offer hope for improved quality of life.
Conclusion
Lewy Body Dementia is a challenging and often underrecognized condition that profoundly impacts individuals and their loved ones. Clinical research is the beacon of hope in the fight against LBD, driving progress in early diagnosis, treatment development, and comprehensive care strategies. By supporting and participating in LBD research, we move closer to a future where this devastating disease is better understood and more effectively managed, ultimately offering hope and improved outcomes for those affected by LBD.
Match with LBD Research Studies Near You
No post found!