High triglycerides, also known as hypertriglyceridemia, is a common medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While triglycerides are a normal component of your blood, elevated levels can increase the risk of various health problems, including heart disease. In this blog, we will explore what triglycerides are, what causes them to become elevated, the associated health risks, and strategies for managing high triglycerides.
What Are Triglycerides?
Triglycerides are a type of fat (lipid) found in your blood. They are the most common type of fat in the body and are primarily derived from the food you eat. Your body also produces triglycerides when it converts excess calories, especially from carbohydrates, into stored fat.
Triglycerides play a crucial role in providing energy for your body’s functions. When you need energy, your body releases triglycerides into the bloodstream, where they can be used as fuel. However, when triglyceride levels are too high, it can lead to health problems.
Triglyceride Levels
In adults, elevated levels of triglycerides are classified by your healthcare provider as:
| Category | Triglyceride Level (mg/dL) |
| Normal | Less than 150 |
| Borderline High | 150 – 199 |
| High | 200 – 499 |
| Very High | 500 and above |
It’s important to note that even if your levels are within the normal range, they can still be considered a risk factor if you have other conditions, such as obesity or diabetes.
In adults, a triglyceride level below 150 mg/dL is considered normal. For young individuals aged 10 to 19, a normal triglyceride level should be below 90 mg/dL.
Your healthcare provider determines your total cholesterol by considering a combination of triglycerides, HDL, and LDL values. If your triglycerides and LDL cholesterol levels are high while your HDL is low, your risk of heart attack and stroke increases.
Causes of High Triglycerides
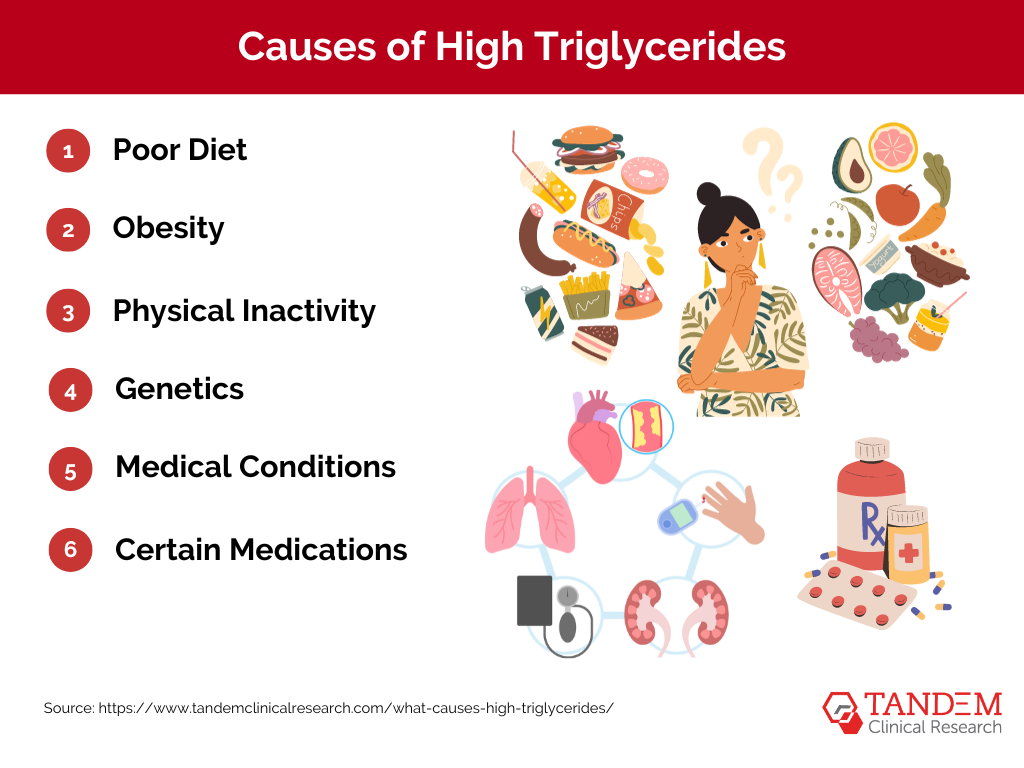
Several factors can contribute to high triglyceride levels, including:
1. Poor Diet
Consuming a diet high in saturated and trans fats, sugar, and refined carbohydrates can lead to elevated triglycerides. Excess calories, especially from sugary beverages and processed foods, can be converted into triglycerides and stored as fat.
2. Obesity
Being overweight or obese is often associated with high triglyceride levels.
3. Physical Inactivity
Lack of regular physical activity can lead to weight gain and elevated triglycerides.
4. Genetics
Some people may have a genetic predisposition to high triglycerides, known as familial hypertriglyceridemia.
5. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, kidney disease, and liver disease, can contribute to high triglycerides.
6. Certain Medications
Some medications, such as steroids, diuretics, and birth control pills, can increase triglyceride levels.
Health Risks Associated with High Triglycerides
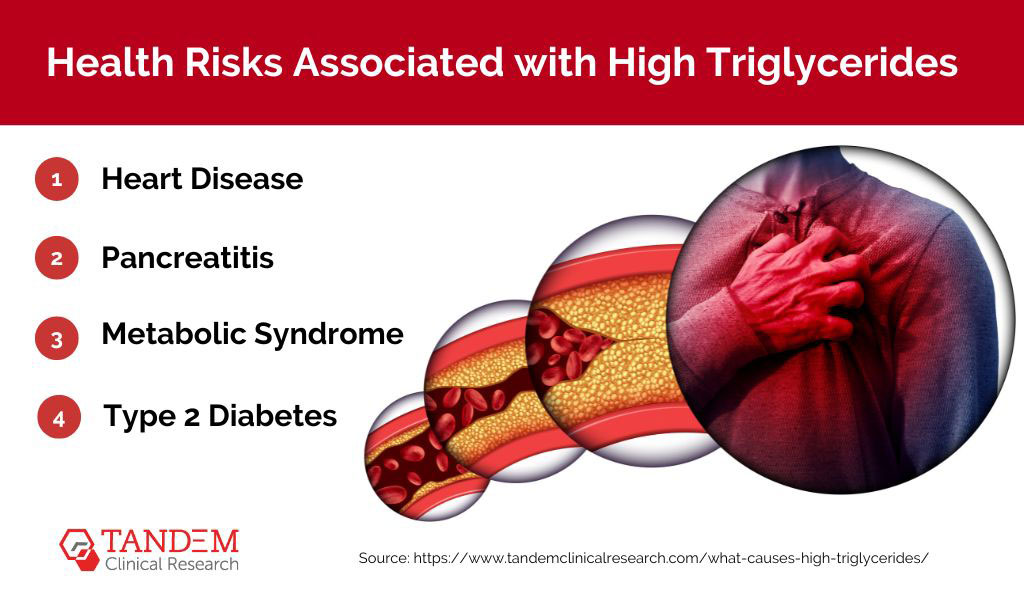
Elevated triglycerides are a concern because they are often associated with an increased risk of various health problems, including:
1. Heart Disease
High triglycerides can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
2. Pancreatitis
Extremely high triglyceride levels can lead to acute pancreatitis, a painful and potentially life-threatening condition.
3. Metabolic Syndrome
High triglycerides are a component of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
4. Type 2 Diabetes
Elevated triglycerides are often found in people with type 2 diabetes, and they can make insulin resistance worse.
Managing High Triglycerides

The good news is that high triglycerides can often be managed through lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medications. Here are some strategies to lower and manage your triglyceride levels:
1. Choose Healthier Food
Adopt a heart-healthy diet that is low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and refined sugars. Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats like those found in fatty fish, nuts, and olive oil.
2. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Losing excess weight through a combination of diet and exercise can significantly reduce triglyceride levels.
3. Exercise Regularly
Engage in regular aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, for at least 150 minutes per week.
4. Limit Alcohol Intake
Excessive alcohol consumption can raise triglycerides. If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
5. Consider Medications
In some cases, your healthcare provider may prescribe medications, such as statins or fibrates, to lower triglyceride levels.
6. Manage Underlying Conditions
If you have conditions like diabetes or hypothyroidism, work with your healthcare team to manage these conditions effectively.
High Triglycerides Clinical Research
Clinical research on high triglycerides has made significant strides in recent years, shedding light on the underlying mechanisms, risk factors, and potential therapies for this common health concern. As researchers continue to explore the complexities of high triglycerides, their findings offer promise for improving the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of associated health complications. In this blog, we will delve into some key aspects of clinical research on high triglycerides, highlighting recent breakthroughs and ongoing investigations.
Recent Breakthroughs in High Triglycerides Research
1. Genetic Insights: Advances in genetics have provided valuable insights into the hereditary factors influencing high triglyceride levels. Research has identified specific gene mutations associated with familial hypertriglyceridemia, helping to better understand the condition and its inheritance patterns.
2. Dietary Impact: Recent studies have highlighted the importance of diet in managing triglyceride levels. Researchers have examined the effects of various diets, such as the Mediterranean diet and low-carbohydrate diets, in reducing triglycerides. These findings offer practical dietary recommendations for individuals with elevated triglycerides.
3. Inflammation and Immune System: Research has uncovered a link between inflammation and high triglycerides. Chronic inflammation in the body can contribute to elevated triglyceride levels. Investigating this connection may open doors to novel therapeutic approaches.
4. Pharmacological Interventions: Clinical trials have evaluated the efficacy of different medications, including triglyceride-lowering drugs like omega-3 fatty acids, fibrates, and novel therapies. These trials aim to identify safe and effective treatments for high triglycerides.
Ongoing Areas of Research
1. Precision Medicine: Researchers are exploring personalized approaches to managing high triglycerides. This involves tailoring treatment plans based on an individual’s unique genetic, metabolic, and lifestyle factors.
2. Gut Microbiome: Emerging research is investigating the role of the gut microbiome in triglyceride metabolism. Understanding how gut bacteria influence triglyceride levels may lead to innovative therapies.
3. Combination Therapies: Studies are ongoing to evaluate the effectiveness of combining different medications or treatment approaches to achieve better triglyceride control while minimizing side effects.
4. Long-term Outcomes: Researchers are conducting long-term studies to assess the impact of high triglycerides on health outcomes, including cardiovascular events and overall mortality. This data can help refine treatment recommendations.
Clinical Research’s Role in Shaping the Future
Clinical research plays a pivotal role in advancing our understanding of high triglycerides and its implications for health. By investigating the complex interplay of genetics, lifestyle, and metabolic factors, researchers aim to develop more targeted and effective treatments. This research not only helps individuals with high triglycerides but also contributes to our broader knowledge of cardiovascular health and metabolic disorders.
Participation in Clinical Trials
If you have high triglycerides or are at risk, consider participating in clinical trials related to this condition. Clinical trials are essential for testing new treatments and therapies, and they rely on the participation of volunteers. By joining a clinical trial, you can contribute to the advancement of knowledge in this field while potentially benefiting from access to cutting-edge treatments.
Conclusion
High triglycerides are a complex health concern with far-reaching implications. Ongoing clinical research is steadily unraveling the mysteries surrounding this condition, offering hope for improved diagnostics, treatments, and prevention strategies. As science continues to progress, the future holds promise for more effective interventions that will ultimately enhance the quality of life for individuals with high triglycerides and reduce the risk of associated health complications.