Gastroparesis is a digestive disorder in which the stomach delays its release of contents into the small intestine. This condition occurs when the muscles in the stomach become impaired or damaged.
Common causes of gastroparesis can include:
- Diabetes
- Nerve damage
- Viral infections
- Certain medications
Gastroparesis is not all that common, impacting roughly 10 men and 40 women out of every 100,000 people. Of these affected patients, each can experience slightly different side effects. Most commonly, symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and a feeling of fullness.
This condition can significantly impact the digestive system, making it difficult for patients to break down foods and properly absorb necessary nutrients. As a result, most people with gastroparesis alter their diets in tandem with medical interventions.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into some basic dietary guidelines for patients with gastroparesis – ones that will help them feel better and lead healthier lifestyles.
How Diet Impacts Gastroparesis
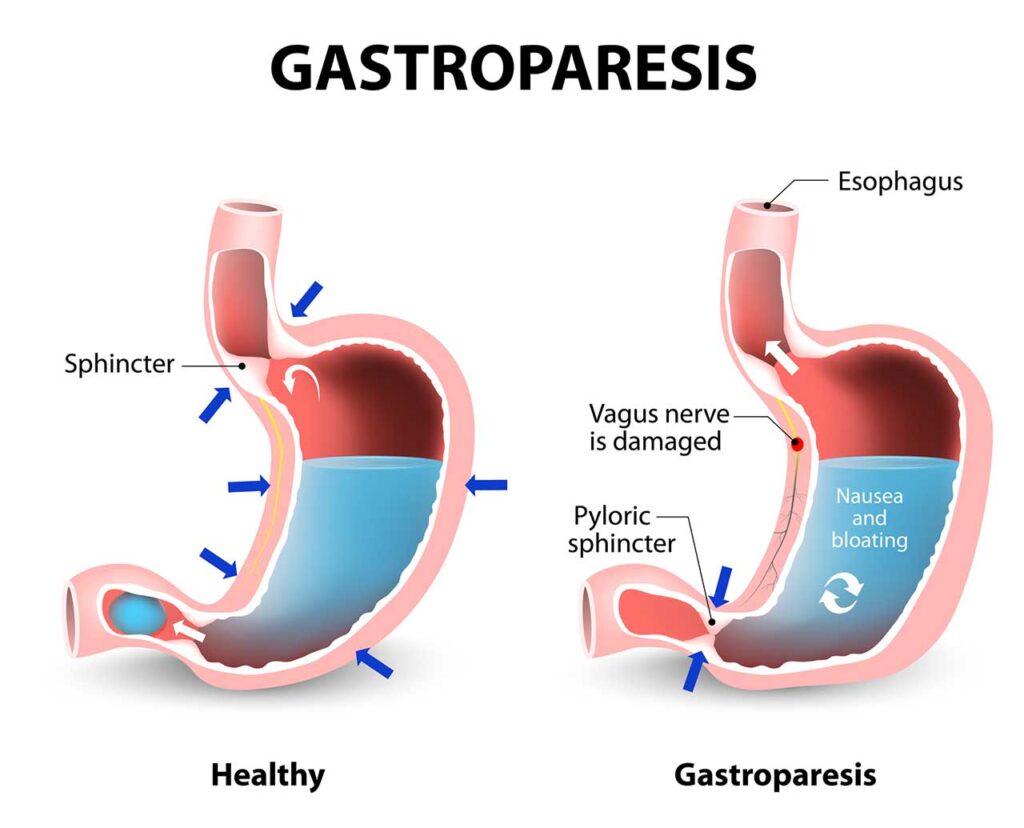
In gastroparesis, the delayed emptying of the stomach disrupts the normal digestive process. Impaired stomach muscle contractions hinder the timely movement of food, and this delayed transit can result in significant difficulties in digestive efficiency and nutrition.
For most patients, dietary modifications are crucial to managing this condition. Not only can making changes to diets help regulate digestion, but it can also alleviate some of the symptoms associated with gastroparesis.
However, patients should always consult a healthcare professional before making changes to their diets.
General Gastroparesis Diet Recommendations

✓ Eat Small Meals More Frequently
One of the best things patients with gastroparesis can do is learn to manage the size of their meals effectively. Eating smaller meals often can reduce the burden on the impaired stomach muscles, contributing to easier digestion and minimizing certain symptoms.
Furthermore, breaking down mealtimes can also help maintain a steadier flow of food into the digestive system. This can result in improved nutrient absorption, which many patients with gastroparesis struggle with.
If you’re looking to try this strategy out, opt for five to six small meals at regular intervals, approximately every 3-4 hours.
✓ Focus on Nutrient-Dense Foods
Balanced nutrition is essential for individuals with gastroparesis. By focusing on the right foods, they can minimize the risk of exacerbating symptoms and boost their reception of essential nutrients.
Most healthcare professionals will recommend focusing on nutrient-dense foods such as:
- Lean proteins (chicken, fish, tofu)
- Cooked vegetables
- Easily digestible fruits (bananas, melons)
- Whole grains
Including a variety of nutrient-rich foods supports overall patient health, but it also helps address potential nutritional deficiencies often present in gastroparesis cases.
✓ Avoid Risky Foods and Drinks
There are some foods that people with gastroparesis simply need to avoid or at least significantly limit. This list predominantly includes:
- High-fat foods
- High-fiber foods
- Greasy foods
- Carbonated beverages
- Caffeinated foods
Avoiding these types of foods and beverages can help minimize the strain on the digestive system and promote better symptom management.
Great Foods to Incorporate in a Gastroparesis Diet
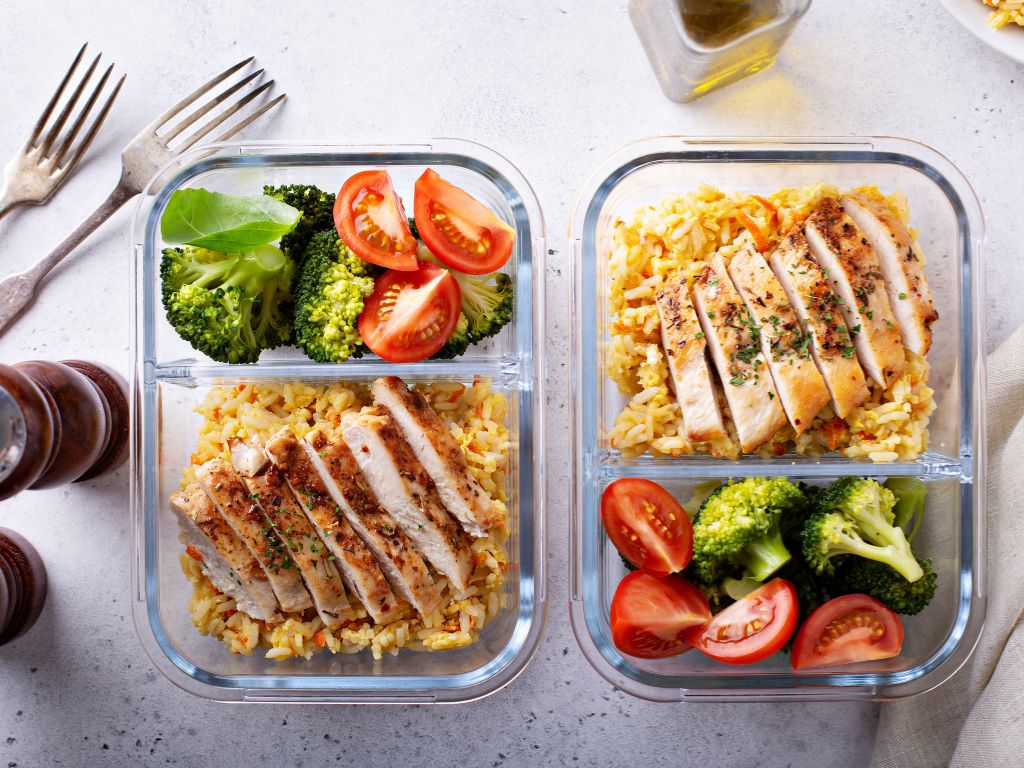

✓ Easily Digestible Proteins
Lean meats and plant-based proteins are generally easier to digest compared to high-fat or tougher protein sources. Stick to meats like chicken and fish and plant-based proteins such as tofu and legumes.
As a bonus, lean meats and plant-based proteins typically move faster through the digestive system, promoting a more efficient gastric emptying process. This reduces the likelihood of symptoms like bloating and discomfort.
✓ Low-Fat Options
In many cases, it’s beneficial to gastroparesis patients to swap high-fat meats, oils, and dairy products for low-fat alternatives. This is also a smart mindset to employ with selecting dressings, sauces, desserts, and snacks.
By reducing the overall fat content in their foods, patients can make digestion a bit easier and potentially alleviate symptoms associated with delayed gastric emptying.
✓ Soft, Cooked Fruits and Veggies
These foods are easier to digest. Furthermore, cooking fruits and vegetables makes them softer, which breaks down their cellular structures and makes them easier for compromised stomach muscles to process.
While dietary fiber in certain fruits and vegetables is essential for overall health, too much fiber can pose challenges. Insoluble fiber, as found in raw fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and nuts, may be particularly problematic as it can contribute to digestive issues.
Always Stay Hydrated

Staying hydrated is critical for individuals with gastroparesis. Intaking enough fluid can help keep symptoms such as nausea and constipation under control.
Rather than drinking large quantities of water at once, focus on sipping small amounts of liquids throughout the day. This can be a helpful strategy to avoid overwhelming the stomach and facilitate better fluid absorption.
Although water is a great choice for staying hydrated, you can also try diluted fruit juices and herbal teas. Try to limit carbonated and caffeinated drinks, which can cause bloating and discomfort.
Bonus Tip: Keep a Food Diary

A daily food and drink journal can be a valuable tool for tracking gastroparesis symptoms and identifying triggers. This information becomes especially beneficial when communicating with healthcare providers, as it provides valuable insights into individualized patterns and responses.
The food and symptom diary doesn’t just help patients – it enables healthcare professionals to identify specific triggers, tailor dietary recommendations, and make more informed decisions regarding treatments.
Have Gastroparesis? Join a Clinical Trial Near You.
Diet plays an essential role in every person’s wellness, but especially in people with digestive conditions like gastroparesis. The more you can tailor your daily food and drink habits to meet your needs, the easier it will be to manage symptoms.
Tandem Clinical Research specializes in connecting patients with gastroparesis and other health conditions with clinical trials. If you live in or near New York City, New Orleans, or Orlando, we’re here to match you with trials.
Managing gastroparesis may be a long-term battle, but cutting-edge research is developing new treatments and solutions for patients. Consider joining a clinical trial today to contribute to this important research.